Embedded Teeth
An embedded teeth is defined as a teeth that has not taken place in the normal occlusion although it was the time for it to erupt and that has remained inside the bone and soft tissue. The formation of an embedded tooth may vary based on parameters such as genotypes, nutrition regimes, the inclusion of the tooth in the function and, ethnic variances etc. It generally appears between the 20 to 23 ages for men and, 21 to 22 years for women.
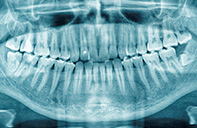
What Are The Indications Of An Embedded Tooth?
Toothache, red and swollen gingiva, headache, a bad taste in the mouth, swelling around the jaw, breath odor, bleeding in the gingiva are among the indications of embedded wisdom teeth.
What Should Be Considered During The Embedded Teeth Procedures?
You should take the medicines recommended by the dentist before the operation. If you use medicines that may prevent the stop of bleeding such as aspirin and anticoagulant etc. you should cease them under the control or your physician before the operation.
What Are The Complications That May Be Experienced After The Embedded Teeth Operations?
- Pain; Pain felt after the embedded teeth surgery is associated with the level of difficulty concerning the respective tooth.
- Edema; Post-surgery edema is at the highest level on the 1st and 2nd days after the operations; it starts to be reduced from the 3rd day and, completely disappears on the 7th day in many cases.
- Trismus (lockjaw): Trismus that may occur following the embedded wisdom teeth treatment is at the maximum level on the 1st and 2nd days after the surgery. It comply regresses on the 7th day; it is reported that it may continue until the 10th day in some cases.
- Infections Bleeding; It is divided into two parts: during the operation (0.7%) and after the operation (0.1%): the reasons may be local or systemic.
 EN
EN
 TR
TR DE
DE AR
AR FR
FR
